


Next: 1 Building an Mx
Up: 6 Univariate Analysis
Previous: 3 Basic Genetic Model
Index
4 Mx Example: Path Coefficients Model
With the introduction from the previous Sections and Chapters, we are
now in a position to set up a simple genetic model using Mx.
The script in Appendix ![[*]](crossref.png) fits a simple univariate
genetic model, estimating path coefficients, to covariance matrices
for two like-sex twin groups: MZ twin pairs reared together, and DZ
twin pairs reared together. The script is written to ignore
information on means. The full path diagram is given in
Figure 6.1
fits a simple univariate
genetic model, estimating path coefficients, to covariance matrices
for two like-sex twin groups: MZ twin pairs reared together, and DZ
twin pairs reared together. The script is written to ignore
information on means. The full path diagram is given in
Figure 6.1
Figure 6.1:
Univariate model for data from monozygotic (MZ) or dizygotic (DZ)
twins reared together (T) or apart (A). Genetic and environmental latent
variables cause the phenotypes 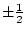 and
and 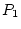
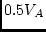 |
We have drawn this figure to correspond to the variables in the model.
The latent genetic and environmental variables and 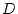 cause
the observed variables
cause
the observed variables 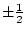 and
and 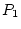 . The script is written to fit
a model with free parameters
. The script is written to fit
a model with free parameters 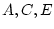 , and
, and 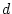 , and fixing
, and fixing 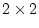 to zero
-- implying that there are no effects of shared environment on BMI.
The script is extensively documented using the comment facility in Mx:
any line beginning with an exclamation mark is interpreted as a
comment. We shall consider this first example Mx script in detail.
Please note that reading this section is not a substitute for
reading in detail the Mx manual [], but merely a quick
introduction to the essentials of a Mx script for genetic
applications.
to zero
-- implying that there are no effects of shared environment on BMI.
The script is extensively documented using the comment facility in Mx:
any line beginning with an exclamation mark is interpreted as a
comment. We shall consider this first example Mx script in detail.
Please note that reading this section is not a substitute for
reading in detail the Mx manual [], but merely a quick
introduction to the essentials of a Mx script for genetic
applications.
Subsections



Next: 1 Building an Mx
Up: 6 Univariate Analysis
Previous: 3 Basic Genetic Model
Index
Jeff Lessem
2000-03-20
![[*]](crossref.png) fits a simple univariate
genetic model, estimating path coefficients, to covariance matrices
for two like-sex twin groups: MZ twin pairs reared together, and DZ
twin pairs reared together. The script is written to ignore
information on means. The full path diagram is given in
Figure 6.1
fits a simple univariate
genetic model, estimating path coefficients, to covariance matrices
for two like-sex twin groups: MZ twin pairs reared together, and DZ
twin pairs reared together. The script is written to ignore
information on means. The full path diagram is given in
Figure 6.1