


Next: 2 Application to Marital
Up: 1 Models for G
Previous: 2 Common Effects G
Index
As with the scalar sex-limitation model, the scalar G
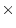 E interaction model equates genetic and environmental
effects on exposed twins to be a scalar multiple of similar effects on
twins who have not been exposed to a modifying environment. As a
consequence, the heritability of a trait remains constant across
exposure groups, and there is no evidence for a genotype
E interaction model equates genetic and environmental
effects on exposed twins to be a scalar multiple of similar effects on
twins who have not been exposed to a modifying environment. As a
consequence, the heritability of a trait remains constant across
exposure groups, and there is no evidence for a genotype
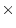 environment interaction. This situation may arise if there
is a mean-variance relationship, and an increase in trait mean under a
particular environmental condition is accompanied by an increase in
phenotypic variation. When this is the case, the ratio of the genetic
variance component and environmental variance component is expected to
remain the same in different environments.
The Mx specification for the scalar G
environment interaction. This situation may arise if there
is a mean-variance relationship, and an increase in trait mean under a
particular environmental condition is accompanied by an increase in
phenotypic variation. When this is the case, the ratio of the genetic
variance component and environmental variance component is expected to
remain the same in different environments.
The Mx specification for the scalar G 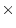 E interaction
model is identical to that used for the scalar sex-limitation model,
except for the addition of MZ discordant pairs. The Mx script in
Appendix
E interaction
model is identical to that used for the scalar sex-limitation model,
except for the addition of MZ discordant pairs. The Mx script in
Appendix ![[*]](crossref.png) illustrates how these pairs may be included.
illustrates how these pairs may be included.



Next: 2 Application to Marital
Up: 1 Models for G
Previous: 2 Common Effects G
Index
Jeff Lessem
2002-03-21
![[*]](crossref.png) illustrates how these pairs may be included.
illustrates how these pairs may be included.